AI Handbook for NGOs
The “AI Handbook for NGOs” is a comprehensive guide we developed to help you start understanding and applying AI in your workflow.
This handbook is complementary material for our ‘AI Crash Course for NGOs’ workshop.
We strongly recommend you to first check out this handbook, then participate in our workshop so that you will have the opportunity to ask questions, engage with content, and share your learnings.
This handbook is a live document last updated on Jan 31, 2025.
Handbook Content
Section 1: Introduction to key AI concepts: What is …?
Section 2: Hands-on AI Experience
Section 3: Discover use cases with examples
Section 1:
Introduction to key AI concepts: What is …?
What is?
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
Artificial Intelligence is any system that simulates human intelligence and skills. AI is not confined to “thinking” like humans but encompasses many human-like capabilities, including learning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding.
Examples: Self-driving cars and virtual assistants.
Machine Learning (ML):
Machine Learning is a specialized subset of AI centered around the concept that machines can learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human direction.
Examples: Systems for product recommendations and fraud detection.
Generative AI (GenAI):
AI systems that can generate new and original content that is similar to their training data, such as text, images, audio, and music.
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP focuses on training AI to understand, interpret, and generate human language text or speech
Large Language Models (LLMs):
LLM is a type of GenAI model specifically trained using massive amounts of text data for NLP tasks.
Prompts:
Prompts are inputs that guide the model in creating output.
System prompt – is the input used to provide initial context and instruction to the LLMs.
User prompt – is the input the user provides, often in the form of text messages sent to the LLMs.
Digital Equity
Fair and inclusive access to technology, the internet, and digital skills ensures everyone can fully participate in society, regardless of socioeconomic, geographic, or demographic barriers.
AI Governance
AI Governance involves the policies, guidelines, and practices established to oversee the ethical development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence.
Section 2:
Quick start with ChatGPT: Hands-on AI Experience
Hands-on AI Experience
How to access ChatGPT?
Getting started with ChatGPT
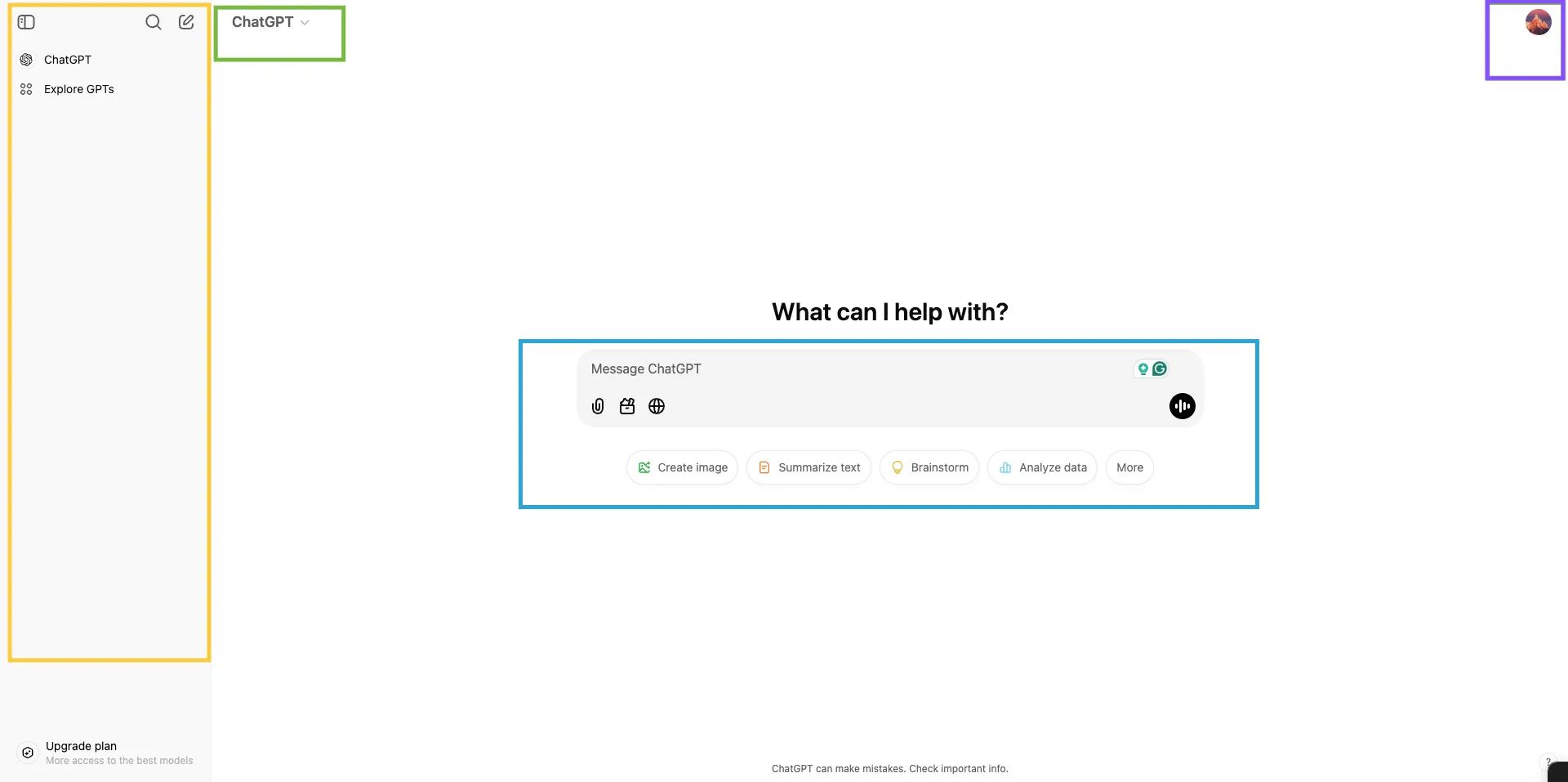
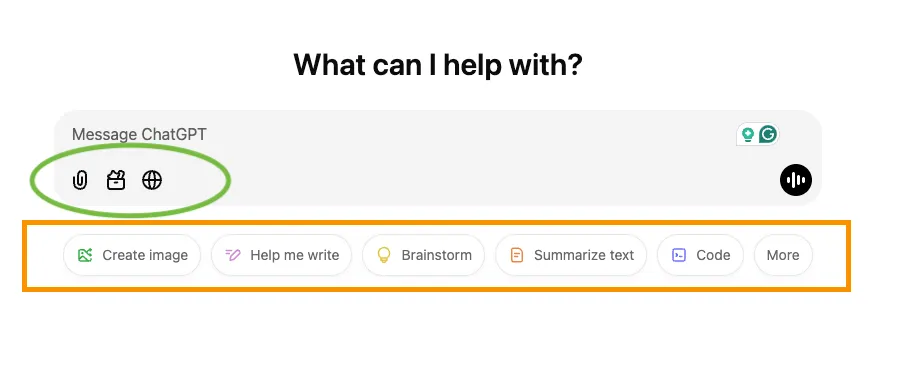
- The text message you enter the BLUE outline is the “prompt”.
- Your chat history is inside the YELLOW outline, you can change the name of the Chat or delete a Chat here.
- By clicking the PURPLE outline area, you can setup everything relate to your chatGPT account.
- The chatGPT model you are using is shown inside the GREEN outline.
Write your first prompt
Prompts are important because they are your input to the AI, and higher-quality input will result in higher-quality output.
Step 1:
Try clicking on a tab within the orange square; ChatGPT will help provide some options to show you how to write a prompt. You can also start by yourself, write an instruction, question, task, or anything else to chatGPT and see what happens.
High-quality prompt → High-quality output
Prompt engineering is designing and crafting prompts for large language models (LLMs) to create the desired outputs.
A quick way to understand this concept is to think of your communication with your colleagues. In this case, you are an excellent manager, and AI is your new teammate.
Some principles to follow as a good communicator:
- Use clear and concise language. Avoid using jargon or technical terms that the model may not understand.
- Provide context. The more context you can provide, the better the model can generate accurate and relevant responses, instead of outputting general descriptions.
- Specify the desired output structure. You can ask the model to generate output in specific structures (e.g., bullet points following given outlines; tables based on given column names).
- Test and refine prompts. This is the process in which you will provide feedback to your AI teammate to help it achieve the goal.
Not-so-good prompt:
Write a grant proposal for AI4NGO
High-quality prompt:
- You are a grant writer for AI4NGO, an NGO that helps other NGOs adopt AI through process improvement, policy support, and training.
- Draft a proposal to secure funding from the EU for an AI safety initiative, focusing on training programs, policy frameworks, and ethical adoption for NGOs.
- Keep it formal, concise, and under 300 words. Highlight AI4NGO’s mission, the importance of AI safety, and expected outcomes.
You can instruct ChatGPT to ask for clarification of your prompt.
Prompting Techniques
Again, let’s start by thinking about how you communicate with your human colleagues. What can you do to help them understand and execute a task?
1. Provide examples
Instead of descriptive instructions, an example provides direct materials for humans and AI to learn from. This is highly effective for generating standardized outputs. Let’s see an example:
Task:
Using these examples, classify the following comments as Positive, Negative, or Neutral, and organize the output into a table with two columns: ‘Comment’ and ‘Sentiment.’ Provide the result as a downloadable Excel file.
Examples:
“This NGO is doing amazing work! I’ll definitely donate again.” → Positive
“I’m disappointed with how funds were allocated this year.” → Negative
“I hope they reach their goal soon.” → Neutral
Comments to be processed:
“Such an inspiring initiative! Keep it up!”
“Why isn’t there more transparency in reporting?”
“Good luck with your campaign!”
Note that using this prompting technique, you can easily process hundreds of comments instead of just the three shown above.1.
2. Provide Organizational Context
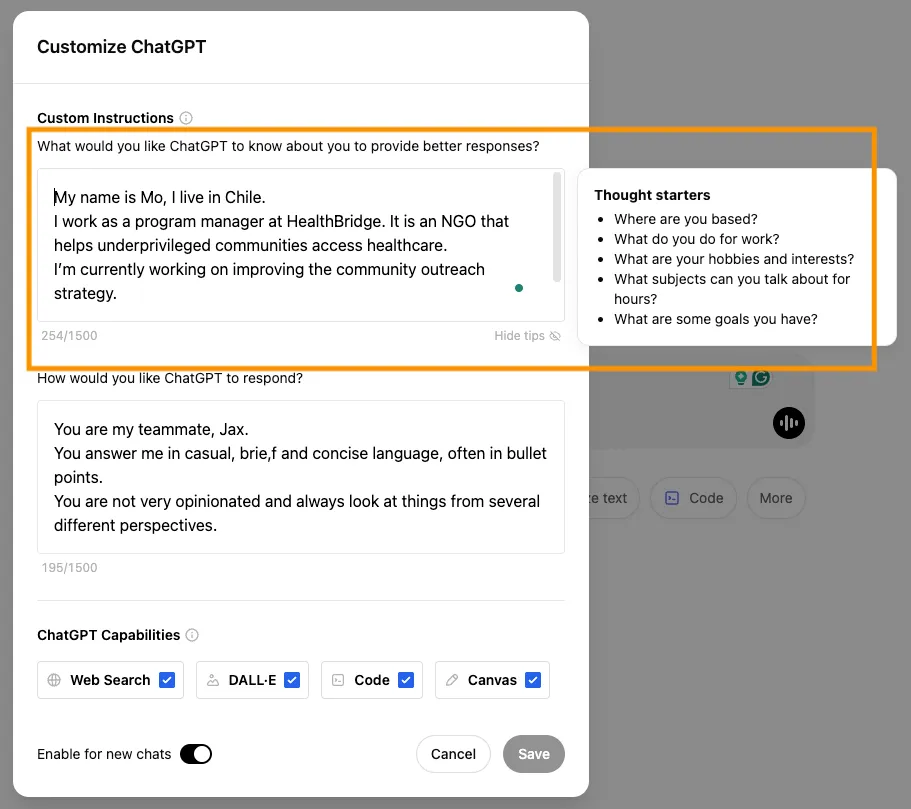
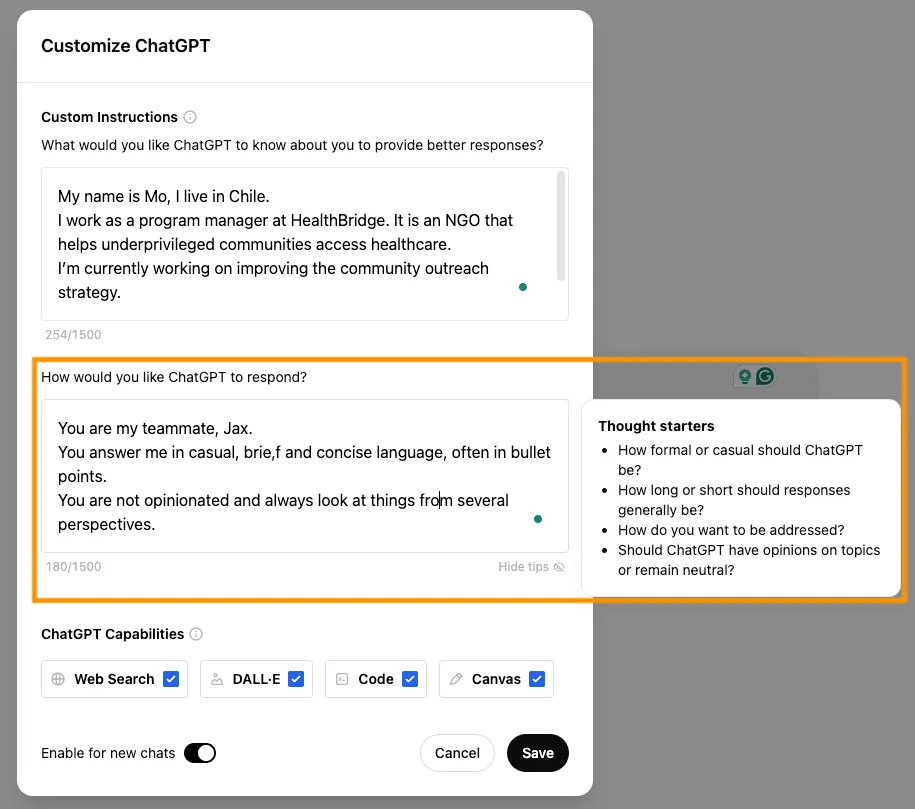
ChatGPT allows you to set custom instructions that will be applicable throughout all your conversations, this is valuable as it makes the responses from AI more relevant to your organization (and you don’t have to write about it repetitively).
Follow the steps below to provide organizational context to ChatGPT.
The Journey of a ChatGPT Power User
Whether you are learning a new instrument or Excel, you can always expect there to be a learning curve. The same is true for AI tools. We observed that in the process of becoming an AI power user, there are three stages of AI function to be unlocked.
Stage 1:
Using AI like a search engine
At the most basic level, ChatGPT can be used as a search engine to find information. Users can simply type in a query, and ChatGPT will return the information. Such as:
“What are the causes of climate change?”
However, this is not the best AI use case due to certain AI limitations (e.g., no real-time data, hallucination). We also advise you to combine the power of AI and search engine to obtain the most updated and valid information.
Stage 2:
Using AI like a Swiss Army Knife
In this stage, you have experimented with different prompts, and you start to have a clearer idea of what the AI is capable of. You also start to write better prompts to instruct AI to execute a variety of text-based tasks, such as:
- Translating documents
- Summarize texts
- Create workshop outline
- Brainstorm your outreach strategy
- Provide feedback for your roadmap
“Generate a table to compare the technology trends between the 2000s – 2020s, and highlight the key social influence of the trends in the last column.”
Stage 3:
Using AI as a Thought Partner
AI has a broad knowledge scope and can be used as an expert agent across many functions and industries. You can set different roles for AI, and it will automatically adopt the common framework, language, and responsibility of that particular role, such as:
- Marketing specialist
- Management consultant
- Personal trainer
- CEO
- Software developer
“You are a program development specialist for NGOs. Our organization is launching an initiative to improve digital literacy in rural schools. Help us design a scalable program outline, identify potential funding sources, and suggest partnerships to amplify impact.”
Disclaimer
This handbook primarily focuses on using ChatGPT, which is easily accessible and combines many functions into one tool.
To learn more about different AI tools, please note that we will regularly update practical tutorials here on our website and social media.
Section 3:
Discover use cases with examples
Use Cases for NGOs
In this section, we will explore some potential AI use cases for NGOs. The AI use cases are coupled with simple prompt examples. To achieve better results, we recommend using the examples below as a starting point and using the knowledge from ‘Hands-on AI Experience’ to further develop your own prompts.
To consolidate our learning about prompting, you will find the examples below all incorporate these six elements:

1. Grant Proposal Writing
Prompt example: “You are a grant-writing specialist (Role). Our NGO focuses on improving digital literacy in underserved rural areas (Context). Draft a grant proposal (Task) for potential donors (Audience) that outlines our program objectives, the implementation plan, and expected outcomes (Scope). Provide the final output as a well-structured document with headers for each section (Output Format).”
2. Targeted Donor Engagement
Prompt example: “You are a fundraising strategist (Role). Our NGO has a donor dataset from the past 5 years (Context). Analyze the data (Task) to identify high-value donors and patterns in their engagement for our donor relations team (Audience). Limit the analysis to donation frequency, amount, and engagement channels (Scope). Deliver the findings as a table with donor segments and suggested engagement strategies (Output Format).”
3. Impact Reporting
Prompt example: “You are a data analyst specializing in nonprofit impact reporting (Role). Our NGO recently completed a digital literacy program for rural schools (Context). Use this dataset of program metrics (Task) to generate insights for board members and stakeholders (Audience). Focus on summarizing key achievements, trends, and quantitative results (Scope). Provide the output as a visually appealing one-page PDF report (Output Format).”
4. Content Creation for Advocacy
Prompt example: “You are a social media campaign strategist (Role). Our NGO is planning a week-long campaign on climate resilience (Context). Create a content plan (Task) targeting the general public and environmental activists (Audience). Focus on post captions, hashtags, and calls-to-action for Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook (Scope). Provide the content plan in a table format, segmented by platform and day (Output Format).”
5. Volunteer Recruitment
Prompt example: “You are a volunteer recruitment expert (Role). Our NGO has a database of volunteer applications from individuals interested in various roles (Context). Match candidates to available tasks (Task) for our volunteer coordinator (Audience). Prioritize skills, availability, and location in the matching process (Scope). Deliver the results as a downloadable Excel table with columns for Name, Suggested Role, and Matching Criteria (Output Format).”
If you want to explore more AI use cases or tools beyond ChatGPT, feel free to contact us at info@ai4ngo.org